Thermal Conductivity
DAIKIN adds thermal conductivity as a special characteristic in our broad line-up of products (plastics, elastomer, coatings, greases...) to help manage upcoming challenges in heat dissipation and transfer.
ABOUT
The needs for thermally conductive polymers
Polymer resins are versatile materials due to properties such as processability and relative strength. However, their relatively low thermal conductivity can present an engineering challenge when applied near a heat source or in metal replacement applications.
The required electrical properties of the resins vary depending on the application. Daikin offers both electrically-insulative and electrically-conductive solutions.
- - Performance and cooling of semiconductors / reliable electronics
The push to pack increasing amount of computing power into ever-smaller semiconductor packages, leads to an increasing engineering challenge to remove the dissipated heat from the electronic components. With the advancement of 5G and high-frequency signals, there is a need to improve thermal conductivity of substrate materials while maintaining low dielectric properties for signal integrity.
- - Automotive electrification
E-powertrain components such as motors, inverters, and battery packs generate less heat than combustion engines; however, their performance and safety are also more sensitive to temperature increases. When designing these components, every layer’s thermal properties need to be considered to secure sufficient heat flow from source to sink.
- - Metal replacement
Plastics are a good alternative to metals due to their lower tooling costs and design versatility. In some metal replacement applications through standard plastics, thermal conductivity is compromised. Plastics with high thermal conductivity are required.
OUR SOLUTIONS
Thermally-conductive, low Dk PFA resin (under development)
This material combines the outstanding properties of PFA resins (best-in-class thermal and chemical stability among melt-processable resins) with a high level of thermal conductivity, while maintaining the low dielectric of fluoro-materials. This unique proposition makes it an excellent material for electronics applications such as PCB substrates or films.
Characteristics
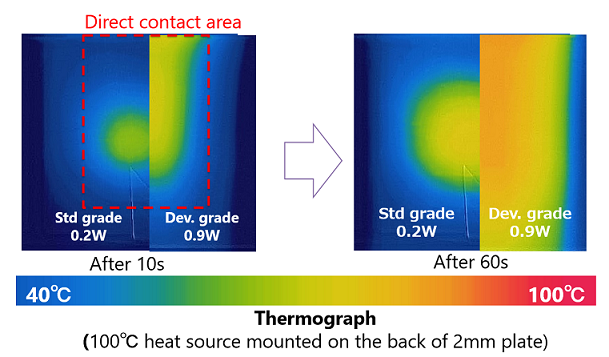
Thermal Properties
| Measurement | Units | Dev. grade | Std. grade | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Thermal Conductivity
|
Thru-plane |
W/m·K |
0.9 |
0.2 |
|
In-plane |
2.8 |
- |
||
|
Thermal Resistance |
Thru-plane | m2·K/W | 3.3x10-3 | 10x10-3 |
Measurement : Periodic radiant heating method
Thermal conductivity (W/m·K)= ρ × Cp × α, ρ: density (kg/m3), Cp: specific heat capacity (J/kg·K), α: Thermal diffusivity (m2·S-1)
Thermal resistance : for 2mm, 1m2
The above numeric values are representative and not guaranteed.
Other Properties
| Item | Condition | Units | Dev. grade | Std. grade |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Dk |
6GHz |
- |
2.6 |
2.1 |
|
Df |
6GHz | x10-4 | 9 | 3 |
|
Volume Resistivity |
JIS K 6911 | Ωcm | ≧1016 | ≧1016 |
|
Dielectric Strengh |
IEC60243-1 /1mmt | kV/m | 44 | 44 |
|
CTI |
IEC60112 /3mmt | V | 600 | 600 |
|
Tensile Strength |
ASTM D 638 | MPa | 27 | 20 |
| Elongation at Break | % | 3 | >100 | |
| Flexural Modulus | ASTM D 790 | GPa | 2.1 | 0.6 |
| Izod Impact Strength |
ASTM D 256 (notched) |
J/m | 32 |
NB |
The above numeric values are representative and not guaranteed.
Thermally-conductive, tough PPS (under development)
PPS compound suitable for metal replacement applications due to its good balance between thermal and mechanical properties.
Material with excellent thermal conductivity and processability below 1mm wall thickness. Further customization of properties for specific applications also possible.
Thermal-physical Properties
| Measurement Direction | Units |
Low-warp Type PPS |
High-strength Type PPS |
General PPS |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Thermal Conductivity |
In-plane |
W/m·K |
12 |
13 |
0.3 |
| Thru-plane | W/m·K | 2.5 | 2.5 | 0.3 | |
Measurement method : Laser flash method
Thermal conductivity (W/m·K)=ρ × Cp × α, ρ: density (g/cm3), Cp: specific heat capacity (J/g·K), α: Thermal diffusivity (m2/s)
The above numeric values are representative and not guaranteed.
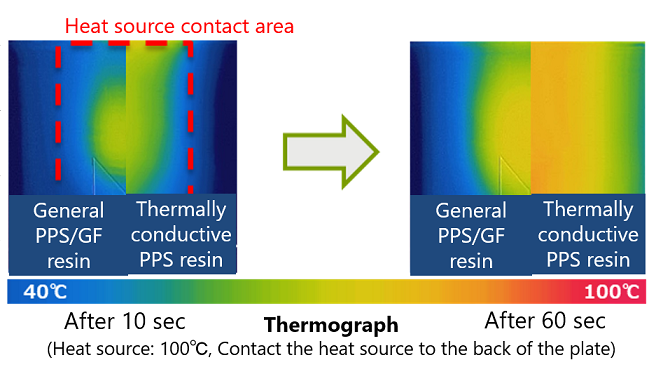
Table of physical properties
In addition to the above thermal and physical properties, it has excellent heat reistance and mechanical properties.
| Item | Condition | Units |
Low-warp Type PPS |
High-strength Type PPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Density |
ISO 1183 |
g/cm3 |
1.7 |
1.7 |
|
Tensile Strength |
ISO 527-2 | MPa | 50 | 70 |
|
Tensile Elongation |
% | 1.1 | 1.1 | |
|
Flexural Strength |
ISO 178 |
MPa | 80 | 100 |
|
Flexural Modulus |
MPa | 16,000 | 20,000 | |
|
Charpy Impact Strength |
ISO 179-1, 2 (unnotched) |
kJ/m2 | 5 | 5 |
| Heat Deflection Temperature (1.8MPa) | ISO 75-2 | ℃ | 240 | 240 |
The above numeric values are representative and not guaranteed.
APPLICATIONS
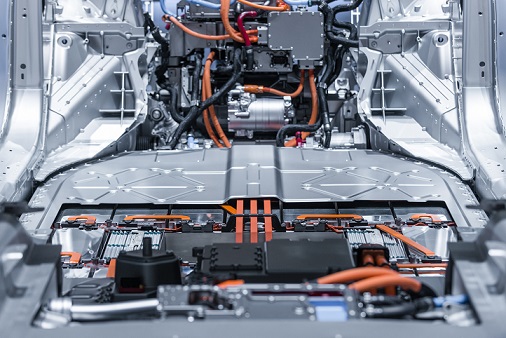

Thermally-conductive materials are increasingly required for heat dissipation and removal in various industries such as automotive, electronics or aerospace. Each specific design requires a matching level of thermal conductivity in the appropriate carrier material.
At DAIKIN, we combine a broad portfolio of materials with our compounding expertise to provide excellent thermal conductivity without compromising the mechanical and chemical properties of fluoro-materials.
- Motor Housings
- Inverter Housings and PCB
- Battery Pack
- Heat Exchangers
- High-frequency PCB Substrates
- Antenna Housings
- Connectors
- Avionics Housings
